- Effect of Side-Chain Substitution on the Physical and Optical Characteristics of TDPP-T Copolymers for Organic Semiconductors
Dae Hong Kim# , Jin Soo Yoo*,# , Junghoon Lee*,†
 , and Kyu Cheol Lee†
, and Kyu Cheol Lee† 
Department of Applied Chemistry, Dong-Eui University, 176 Eomgwangro, Busan 47184, Korea *Division of Chemical Engineering, Dongseo University, Busan 47011, Korea
- 유기반도체용 TDPP-T 공중합체의 곁사슬 치환이 물리적, 광학적 특성에 미치는 영향
동의대학교 응용화학과, *동서대학교 화학공학부
Reproduction, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form of any part of this publication is permitted only by written permission from the Polymer Society of Korea.
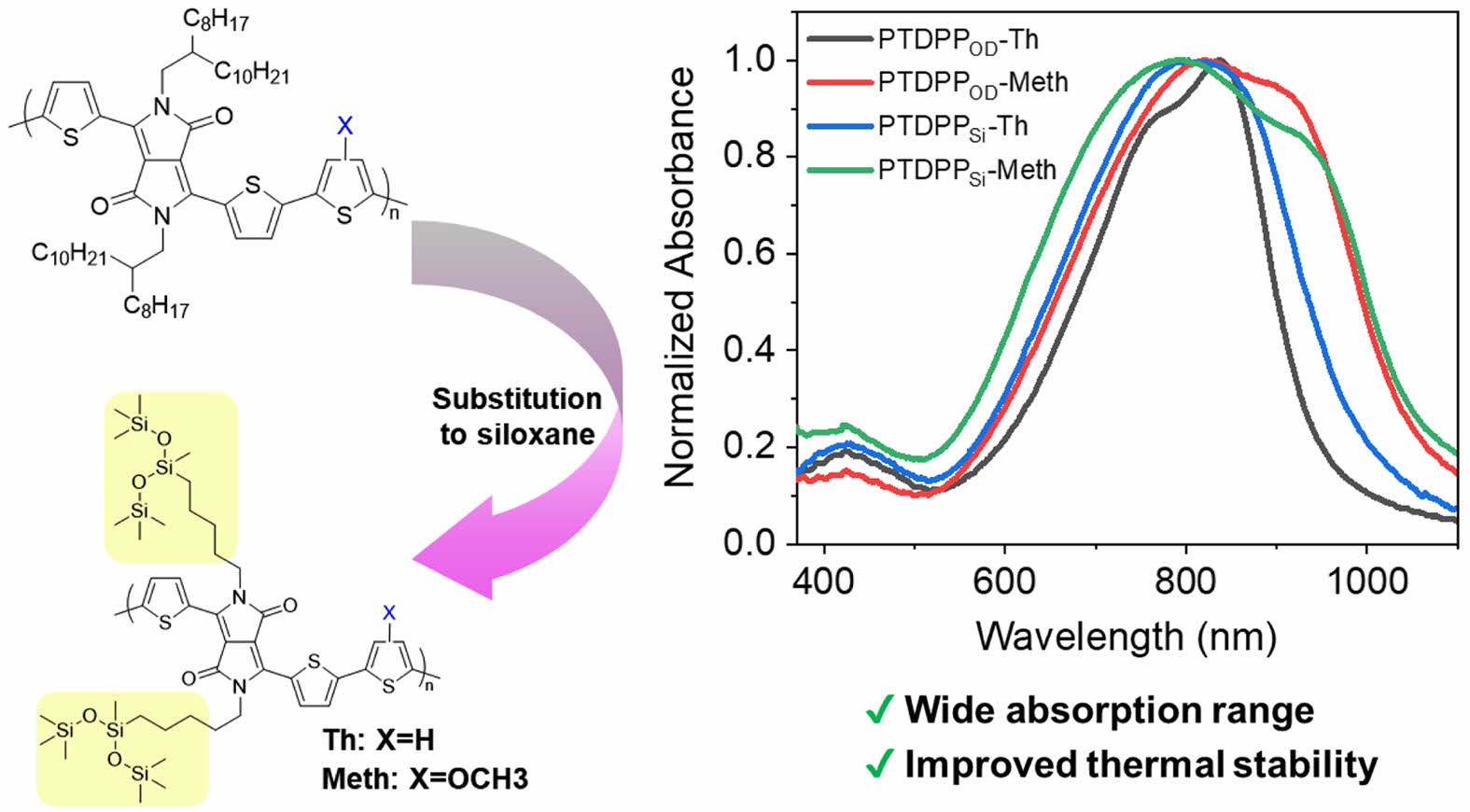
This study aimed to investigate the physical and chemical properties resulting from the introduction of siloxane or methoxy group substituents in four copolymers, which were synthesized using thiophene(T) or methoxy thiophene and thienyl diketopyrrolopyrrole.Polymers containing siloxane group showed a wider absorption range and higher thermal stability than polymers with hydrocarbons. These results can open a possibility to be used as materials for high stable organic semiconductors.
본 연구에서는 thiophene(T) 또는 methoxy thiophene과 탄화수소 또는 실록세인(siloxane)을 곁사슬로 갖는 thienyl diketopyrrolopyrrole(TDPP)를 Stille 커플링 중합법으로 네 가지의 유기 반도체용 공중합체를 합성하여 실록세인 곁사슬과 methoxy 기에 따른 물리적 및 화학적 특성을 확인하였다. Siloxane 기를 갖는 고분자의 경우는 탄화수소를 갖는 고분자보다 넓은 흡수 범위와 높은 열 안정성을 보여 주었다. 이런 결과는 고안정성 유기반도체용 재료로써 활용할 수 있음을 의미한다.
We examined how siloxane and methoxy substituents affected the physical and chemical characteristics of four thiophene (T) or methoxy thiophene and diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP) copolymers. Polymers containing siloxane chain groups have better thermal stability and absorption, suggesting they might be used to make very stable organic semiconductors.
Keywords: conjugated polymer, diketopyrrolopyrrole, thermal stability, organic semiconductor, siloxane.
저자들은 이해상충이 없음을 선언합니다.
다음과 관련된 정보(GPC, UV-Vis-NIR spectrum(DFT))는 다음 사이트에서 확인 가능(http:// journal.polymer-korea.or.kr).
PK_2025_049_05_634_Supporting_Information.pdf (410 kb)
Supplementary Information
금속과 같은 전기적 특성을 갖는 전도성 고분자(conductive polymer)는 금속 및 반도체의 전자기적, 광학적 성질을 가지고 있다. 구조적 특징으로는 단일 결합과 다중 결합이 교대로 반복하여 π-공액(conjugation) 구조를 형성하며, 이에 따라 전자가 분자 내 또는 분자 간 자유롭게 흐를 수 있으므로 공액 고분자(conjugated polymer)라고도 부른다.1,2 우수한 광학 및 전기적 특성, 가격 경쟁력, 경량화 등의 장점을 갖는 전도성고분자는 유기발광다이오드(organic light-emitting diodes, OLEDs),3 유기 태양전지(organic solar cells, OSCs),3-5 유기전계효과트랜지스터(organic field-effect transistors, OFETs),6 열전소자(organic thermoelectric device)7 등의 다양한 소자에 적용하는 연구가 진행되고 있다. 특히, 높은 용해도로 인해 용액 공정에 용이하며 우수한 유연성을 가지고 있어 전통적인 진공 증착 공정이 필요 없이 용액 캐스팅(solution casting), 롤투롤(roll-to-roll) 등의 간단한 공정으로 소자에 적용할 수 있어 많은 주목을 받고 있다.8,9
현재까지 보고된 많은 공액 고분자는 전자가 풍부한 전자주개(donor, D)와 전자가 부족한 전자받개(acceptor, A)가 교대로 구성된 교대배열 공중합체(alternating copolymer)를 갖는 구조적 특징을 갖는다. 전자주개로는 싸이오펜(thiophene), 싸이에노싸이오펜(thienothiophene, TT),10 싸이오펜바이닐싸이오펜((E)-2-(2-(thiophen-vinyl)thiophene, TVT)11 등이 있으며, 전자받개로는 다이케토피롤로피롤(diketopyrrolopyrrole, DPP), 아이소인디고(isoindigo, IID),12 나프탈렌다이이미드(naphthalenediimide, NDI)13 등이 있다. 그 중 DPP는 구조적 안정성, 광범위한 흡수, 합성의 용이성, 높은 전하이동도 등의 장점을 갖기 때문에 다양한 D-A 조합으로 유기 전자 소자에 많이 활용되고 있으며,6,14,15 소량의 다른 구조를 첨가하여 고신축성 유기 반도체 소자6로써 많은 관심을 받고 있다. 이와 더불어 다양한 곁사슬(side chain) 도입은 메인 골격의 변화를 주지 않고 용해도(solubility), 모폴로지(morphology), 전하이동도, 전자기적, 광학적 성질은 영향을 미치기 때문에 최근에 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있다.16,17 특히 실록세인(siloxane)구조를 공액 고분자에 도입하였을 때 용해도의 향상과 더불어,18 치환기의 상호 작용에 의해 분자-분자 간 감소한 거리가 전하이동도 향상에 기여하며 탄화수소 치환기와 비교하였을 때 구조적으로 습한 환경(humid atmosphere)에서 안정성을 갖기 때문에 유기태양전지, 유기전계효과트랜지스터, 물분해(water-splitting)19 등에 활용되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 곁사슬이 공액 고분자의 광학적성질, 열적 안정성, 전기화학적 성질 등에 어떠한 영향을 미치는지 조사하기 위하여 DPP 구조의 양쪽에 싸이오펜을 갖는 thienyl DPP 구조와 싸이오펜을 활용하여 서로 다른 4종의 공액 고분자인 PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPSi-Th, PTDPPSi-Meth를 마이크로 웨이브를 이용한 Stille 중합법으로 합성하였다. 합성한 고분자의 구조를 확인하기 위하여 핵자기공명법(nuclear magnetic resonance, NMR)과 푸리에 변환 적외선 분광법(Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, FTIR)을 측정하여 분석하였으며, 자외선 분광 분석법(UV/vis spectrophotometry)으로 광학적 성질을 측정하였다. 순환전압전류법(cyclic voltammetry, CV)을 이용하여 에너지 준위를 구하였으며 겔 투과 크로마토그래피(gel permeation chromatography, GPC) 및 열중량 분석(thermogravimetric analysis, TGA)을 통해 고분자의 분자량 및 열적 안정성을 확인할 수 있었다.
시약, 재료, 기기. 중간체와고분자 합성에 필요한 시약은 시그마알드리치(Sigma-Aldrich, USA)사, ㈜한국피셔과학(Thermo Fisher Scientific, Korea), 도쿄화성공업(TCI, Japan) 등에서 구매하였고, 별도의 추가 정제 없이 사용하였다. 그 중 반응 용매는 ACS 등급을 사용하였다. 2,5-bis(trimethylstannyl)thiophene(M1)은 시그마알드리치에서 구매하였고, (3-methoxythiophene-2,5-diyl)bis(trimethylstannane)(M2), 3,6-bis(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-2,5-bis(2-octyldodecyl)pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4(2H,5H)-dione(M3)는 SunaTech Inc.(China)에서 각각 구매하였다. 3,6-bis (5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-2,5-bis(5-(1,1,1,3,5,5,5-heptamethyltrisiloxan-3-yl)pentyl)pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4(2H,5H)-dione(M4)는20 문헌을 참고하여 합성하였다. 합성한 고분자의 화학 구조는 600 MHz NMR(600MHz Agilent Superconducting FT-NMR Spectrometer System, Agilent, USA)로 측정하여 확인하였다. 자외/가시광선 분광광도계(OPTIZEN POP, mecasys, Korea)를 사용하여 고분자의 광학적 특성을 클로로포름(chloroform, CF)에 녹인 용액 상태(solution state)와 스핀 코터(spin coater EF-4op, 이플렉스, Korea)를 이용하여 석영판(quartz plate)에 코팅한 필름 상태로 각각 측정하였다. 고분자의 수 평균 분자량(Mn)과 다분산지수(poly dispersity index, PDI)는 polystyrene을 기준으로 하고 tetrahydrofuran(THF)을 이동상으로 하여 GPC(Agilent 1200S/miniDAWN TREOS, Agilent/Wyatt, USA)를 통해 측정하였다. 전기화학적 특성은 CV(Versa STAT3, AMETEK, USA)으로 확인하였다. 기준전극(reference electrode), 작업전극(working electrode), 상대전극(counter electrode)은 Ag/Ag+, glassy carbon(GC) disk, platinum(Pt) wire로 각각 사용하였으며, 100 mV/s의 속도로 측정하였다. 전해질은 acetonitrile(ACN)에 tetra-n-butylammonium hexafluorophosphate (n-Bu4NPF6)를 용해시켜 0.1 M의 농도로 만들어 사용하였고, 기준전극(Ag/Ag+)은 페로센/페로세늄(ferrocene/ferrocenium) 산화/환원 반응으로 교정하였으며, 산화 전위는 진공수준일 때 -4.8 eV를 기준으로 설정하였다. 고분자의 HOMO와 LUMO 준위는 HOMO(eV) = -(E(oxi)onset - E1/2 (ferrocene) + 4.8)와 LUMO(eV) = -(E(red)onset - E1/2(ferrocene) + 4.8)의 식으로 각각 계산하였다. 고분자의 HOMO/LUMO 준위, 분자구조의 최적화, 광학적 성질 예측 등을 확인하기 위해 밀도범함수 이론(density functional theory, DFT)(Gaussian 16, Becke three-parameter Lee-Yang-Parr(B3LYP) function, 6-31G basis set)을 활용하여 계산하였다. 고분자의 열적 특성은 열중량 분석 TGA(TGA N-1000, 신코, Japan)를 사용하여 질소 분위기에서 상온(약 16 ℃) 에서부터 900 ℃까지의 온도범위로 10 ℃/min의 속도로 승온하였을 때 온도에 따른 질량 감소율을 측정하였다.
고분자 합성(공통). M1 또는 M2 그리고 M3 또는 M4, Pd(PPh3)4, anhydrous toluene 5 mL를 30 mL 마이크로웨이브 반응 용기에 첨가하였다. 반응물은 Anton-Paar 마이크로웨이브를 사용하여 110 ℃에서 120분 동안 반응하였고, 50 ℃까지 온도를 낮춘 후 300 mL methanol에 침전시켰고, 마이크로필터(0.45 μm 필터 종이)를 사용하여 정제되지 않은 고체를 얻었다. 그런 후 고분자에 포함된 불순물과 낮은 분자량을 갖는 부분을 제거하기 위해서 Soxhlet extractor를 이용하여 methanol, acetone에서 각 24시간 녹아 나오는 부분을 순차적으로 제거하였고, 마지막으로 chloroform으로 추출한 용액을 농축(10 mL)하여 methanol에서 침전, 마이크로 여과, 진공건조를 하여 고분자를 얻었다.
Poly[3-([2,2'-bithiophen]-5-yl)-2,5-bis(2-octyldodecyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4(2H,5H)-dione] (PTDPPOD-Th).
M1(120 mg, 0.294 mmol), M3(300 mg, 0.294 mmol)(수득률 = 75%) Pd(PPh3)4(10 mg, 8.8 μmol), Mn = 66.3 kg/mol, Mw = 122.3 kg/mol, PDI = 1.85. 1H NMR(CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ ppm 9.31-8.59(br, 2H), 7.21-6.67(br, 4H), 4.41-3.44(br, 4H), 1.53-0.98(br, 66H), 0.97-0.70(br, 12H).
Poly[(4'-methoxy-[2,2'-bithiophen]-5-yl)-2,5-bis(2-octyldodecyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4(2H,5H)-dione] (PTDPPOD-Meth).
M2(130 mg, 0.294 mmol), M3(300 mg, 0.294 mmol)(수득률 = 70%) Pd(PPh3)4(10 mg, 8.7 μmol), Mn = 14.2 kg/mol, Mw = 20.5 kg/mol, PDI = 1.44. 1H NMR(CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ ppm 9.34-8.39(br, 2H), 7.21-6.27(br, 4H), 4.38-3.62(br, 7H), 1.54-0.98 (br, 66H), 0.97-0.70(br, 12H).
Poly[3-([2,2'-bithiophen]-5-yl)-2,5-bis(5-(1,1,1,3,5,5,5-heptamethyltrisiloxan-3-yl)pentyl)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4(2H,5H)-dione] (PTDPPsi-Th).
M1(118 mg, 0.289 mmol), M4(300 mg, 0.289 mmol)(수득률 = 50%) Pd(PPh3)4(10 mg, 8.7 μmol), Mn = 173.6 kg/mol, Mw = 1080.0 kg/mol, PDI = 6.22. 1H NMR(CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ ppm 9.22-8.32(br, 2H), 7.03-6.13(br, 4H), 4.96-3.38(br, 4H), 1.50-1.07(br, 12H), 0.53-(-)0.28(br, 46H).
Poly[2,5-bis(5-(1,1,1,3,5,5,5-heptamethyltrisiloxan-3-yl)pentyl)-3-(4'-methoxy-5'-methyl-[2,2'-bithiophen]-5-yl)-6-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4(2H,5H)-dione] (PTDPPsi-Meth).
M2(118 mg, 0.289 mmol), M4(300 mg, 0.289 mmol)(수득률 = 70%) Pd(PPh3)4(10 mg, 8.7 μmol), Mn = 173.6 kg/mol, Mw = 1080.0 kg/mol, PDI = 6.22. 1H NMR(CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ ppm 9.10-8.20(br, 2H), 7.10-6.10(br, 4H), 4.33-3.50(br, 7H), 1.53-1.16(br, 12H), 0.51-0.06(br, 46H).
고분자 합성. Scheme 1에서 보는 것과 같이 2,5-bis(trimeth- ylstannyl)thiophene(M1) 또는 (3-methoxythiophene-2,5-diyl) bis(trimethylstannane)(M2)과 3,6-bis(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-2,5-bis(2-octyldodecyl)pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4(2H,5H)-dione (M3) 또는 3,6-bis(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-2,5-bis(5-(1,1,1,3,5,5,5- heptamethyltrisiloxan-3-yl) pentyl) pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4 (2H,5H)-dione(M4)를 각각 1:1 몰수 비율로 toluene에 용해 시켜 Pd(PPh3)4을 촉매로 사용하여 Stille 중합 반응(Stille cross coupling polymerization)을 통해 4종의 전도성 고분자 PTDPPOD-Th(M1, M3), PTDPPOD-Meth(M2, M3), PTDPPsi-Th(M1, M4), PTDPPsi-Meth(M2, M4)를 각각 75%, 70%, 50%, 70%의 수득률로 합성하였다. Gel permeation chromatography(GPC)을 통해 합성한 고분자의 수평균 분자량(Mn)을 측정하였고, 각각 66.3, 14.2, 173.6 그리고 16.7 kg/mol로 측정되었다(Table 1, Figure S1, Table S1).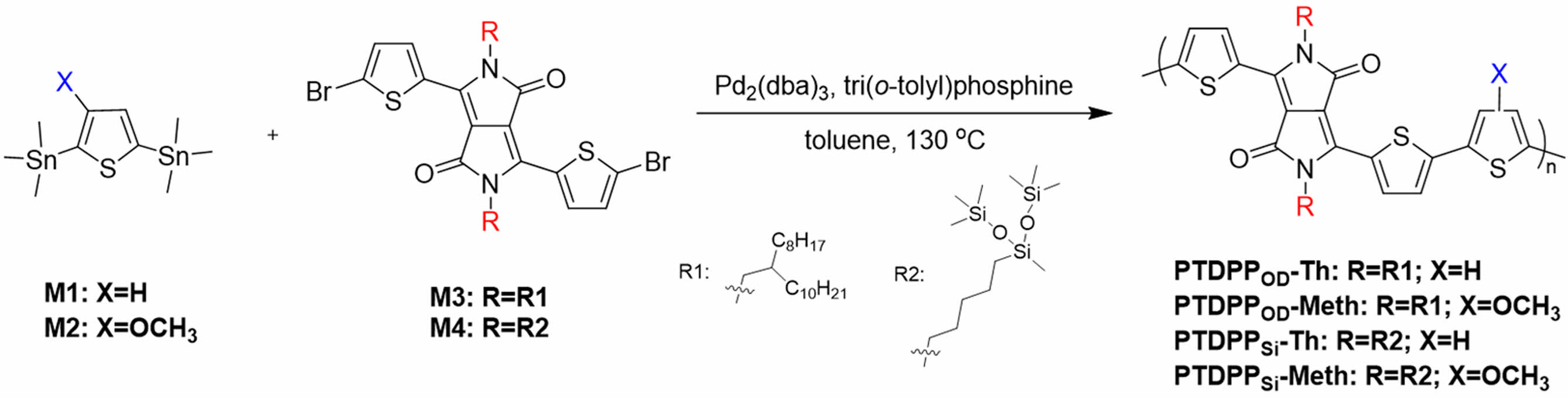
Scheme 1. Synthetic procedures for PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th and PTDPPsi-Meth.
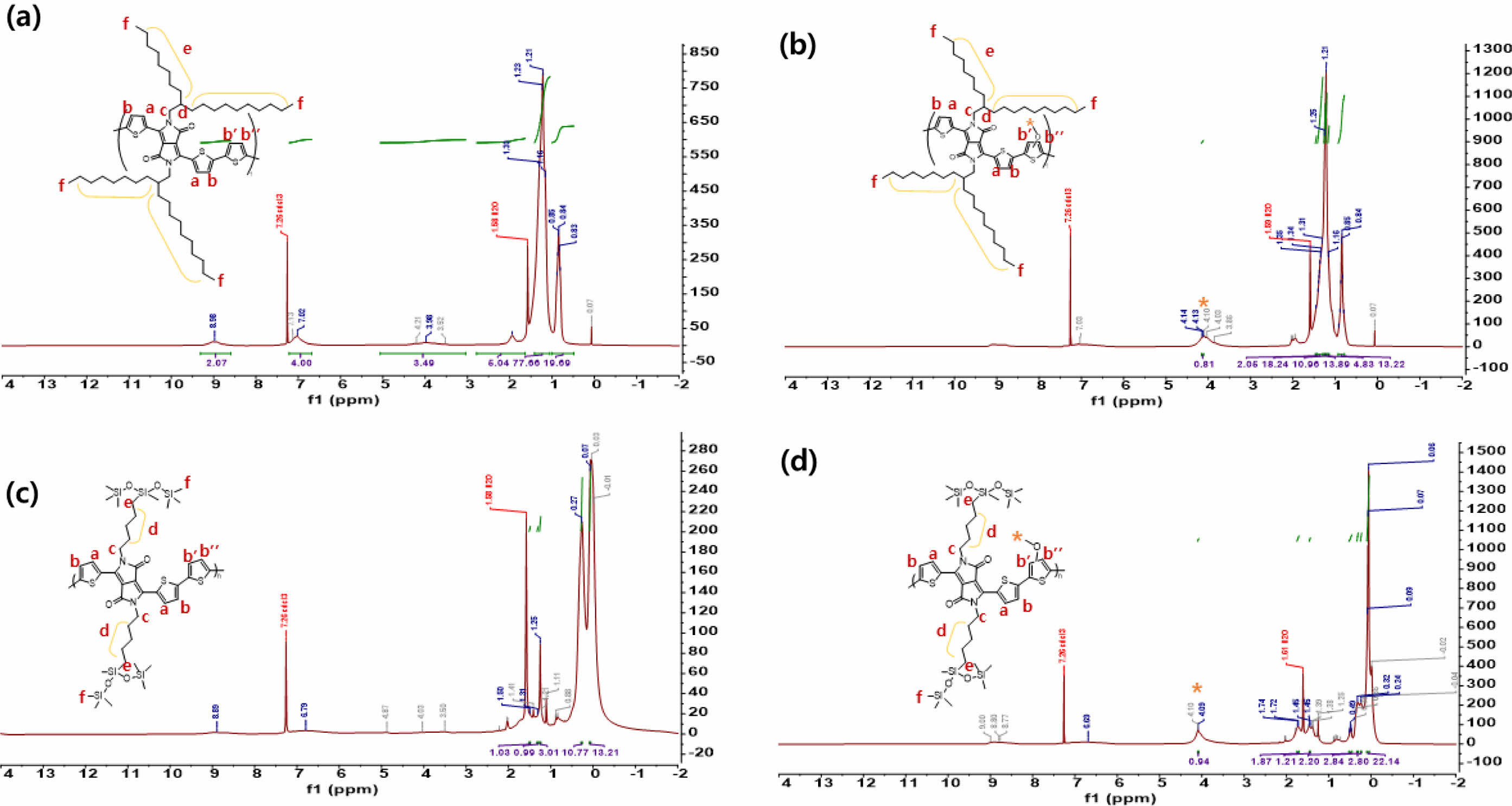
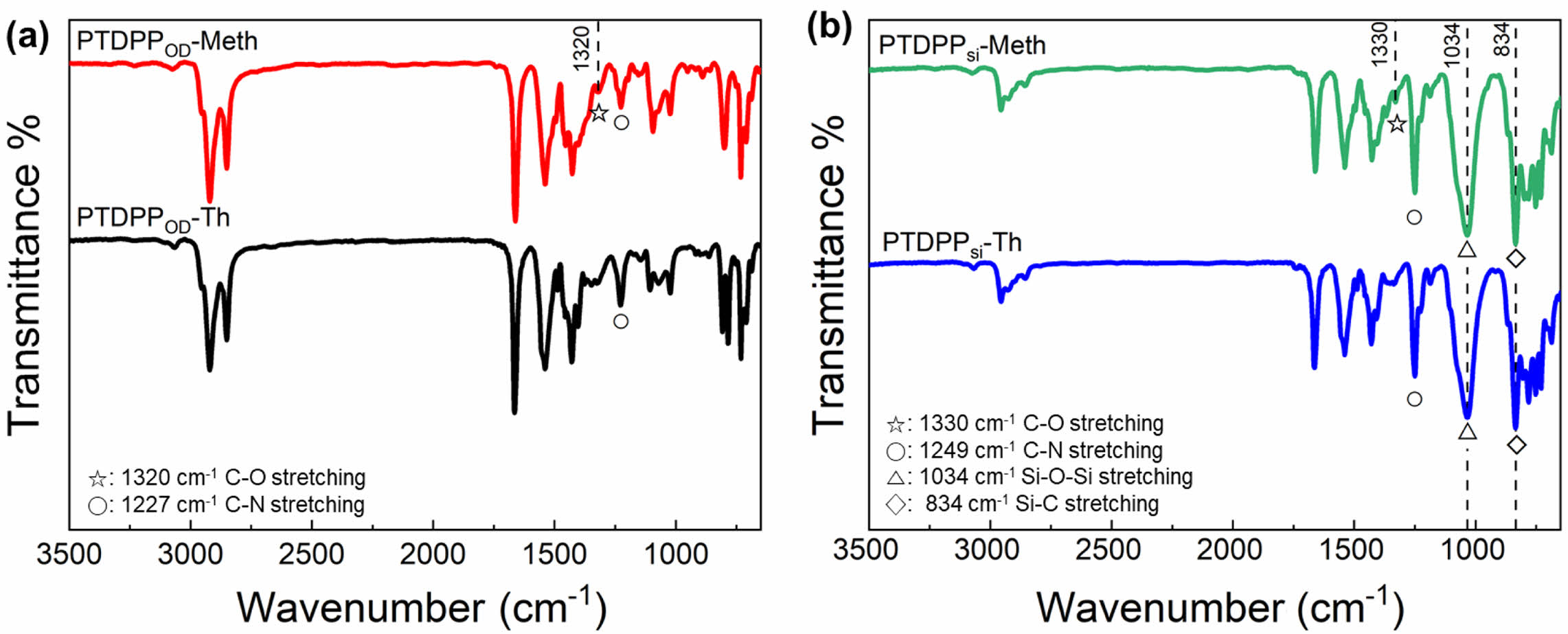
고분자 구조 분석.합성한 고분자의 화학적 구조를 분석하기 위해 600 MHz 푸리에 변환 핵자기 공명 분석을 CDCl3 용매를 사용하여 진행하였다(Figure 1). PTDPPOD-Th와 PTDPPOD-Th의 thienyl diketopyrropyrrole(DPP)의 싸이오펜(thiophene)과 그 옆의 싸이오펜의 방향족 고리의 수소는 9.31-8.59, 7.21-6.67 ppm 영역과 9.34-8.39, 7.21-6.27 ppm 영역에서 각각 나타나는 것을 확인했고, 알킬사슬의 수소는 4.41-3.44, 1.53-0.98, 0.97-0.7 ppm 영역과 4.38-3.62, 1.54-0.98, 0.94-0.7 ppm 영역에서 각각 나타나는 것을 확인하였다. PTDPPsi-Th와 PTDPPsi-Meth의 DPP 양쪽 싸이오펜과 그 그 옆 싸이오펜의 방향족 고리의 수소는 9.22-8.32, 7.03-6.13 ppm 영역과 9.1-8.2, 7.1-6.1 ppm 영역에서 각각 나타나는 것을 확인했고, 알킬사슬 및 실록세인 사슬의 수소는 4.96-3.38, 1.50-1.07, 0.53-(-)0.28 ppm 영역과 4.33-3.5, 1.53-1.16, 0.51-0.06 ppm에서 나타나는 것을 확인하였다. PTDPPOD-Meth와 PTDPPsi-Meth는 methoxy의 수소로 인해 4.38-3.62 ppm과 4.33-3.5 ppm에서 각각 sharp한 피크를 확인할 수 있었고, PTDPPOD-Th와 PTDPPsi-Th의 4.41-3.44 ppm과 4.96-3.38 ppm에서는 매우 약한 피크만 관찰되어 methoxy group에 따른 구조적 차이를 확인할 수 있었다. FT-IR을 통해 합성한 고분자의 작용기와 구조적 특성을 확인하였고 Figure 2에 나타내었다. PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th 그리고 PTDPPsi-Meth의 sp2/sp3 혼성 탄화수소의 C-H 신축(stretching) 진동 피크를 3074/2920, 3065/2920, 3066/2955 그리고 3074/2955 cm-1 영역에서 각각 관찰하였고, DPP의 이미드(imide)에 해당하는 C=O 신축진동 피크를 1663, 1660, 1663, 1660 cm-1 영역에서 각각 확인하였다. DPP의 방향족 아민(aromatic amine)에 해당하는 C-N 신축진동 피크가 1227, 1227, 1249, 그리고 1249 cm-1 영역에서 관찰되어 고분자의 구조적 특성을 확인할 수 있었다. PTDPPsi-Th와 PTDPPsi-Meth는 siloxane곁사슬로 Si-O-Si, Si-C 신축진동 피크가 동일하게 1034 cm-1와 834 cm-1 영역에서 확인되었고, PTDPPOD-Meth와 PTDPPsi-Meth는 methoxy로 인한 alkyl aryl ether에 해당하는 C-O 신축진동 피크가 1320, 1330 cm-1 영역에서 각각 확인하였다.
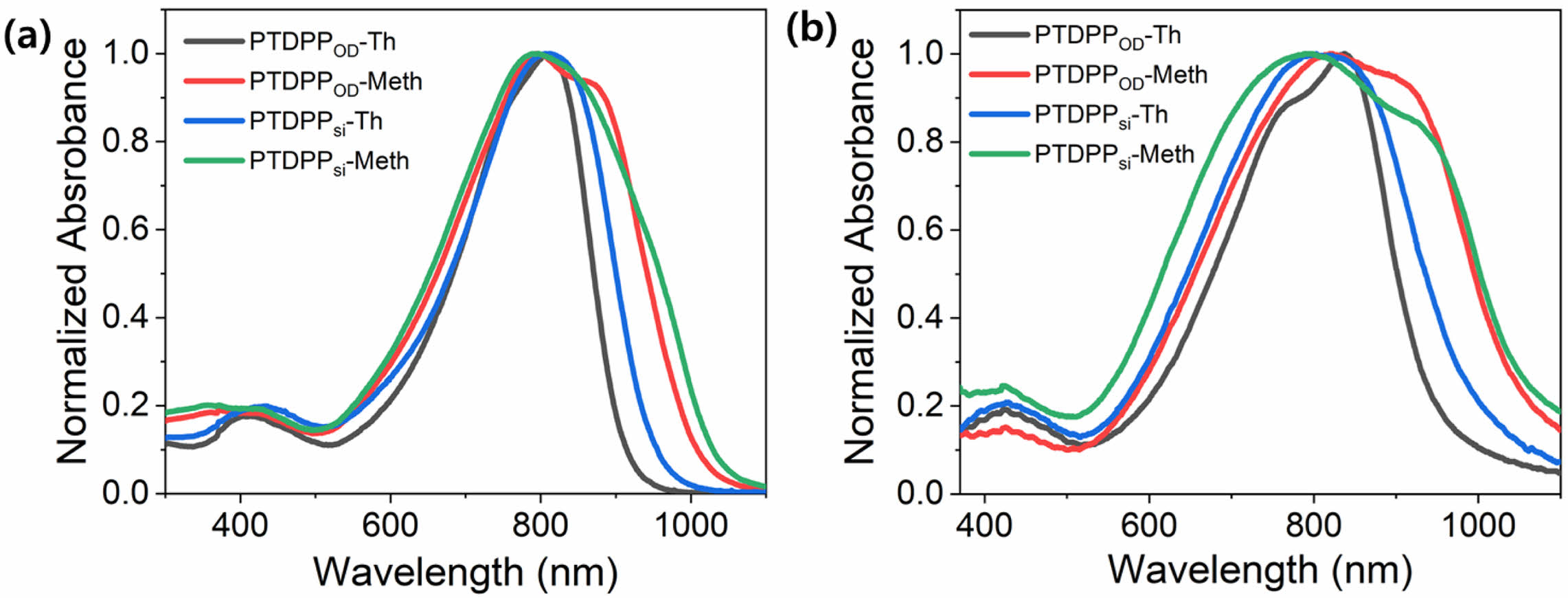
광학적 특성. Methoxy 기의 치환에 따른 고분자의 광학적 성질을 관찰하기 위해 자외/가시광선 분광광도계(UV-Vis spectrophotometer)를 이용하여 용액 상태와 박막 상태에서 각각 측정하였고 그 결과를 Figure 3에 나타내었다. 박막 상태에서 Tauc plot을 통해 고분자의 광학적 밴드갭을 계산하였고, PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th, PTDPPsi-Meth의 밴드갭은 1.36, 1.22, 1.30, 그리고 1.20 eV을 갖는 것을 확인하였다(Table 1, Figure S2). PTDPPOD-Th와 PTDPPsi-Th는 용액상태 (a)에서 π–π* 전하이동(π–π* transition) 피크를 상대적으로 짧은 파장인 380-470 nm에서 확인하였고, PTDPPOD-Meth와 PTDPPsi-Meth는 그보다 넓은 330-470 nm에서 확인하였다. 박막상태 (b)에서는 4개의 고분자 모두 350-500 nm에서 π–π* 전하이동(π–π* transition) 피크를 확인하였다. 용액상태/박막상태에서 측정한 PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th와 PTDPPsi-Meth의 최대흡수파장(λmax)은 812, 795, 809, 797/837, 821, 803, 그리고 794 nm로 확인하였다. 4개의 고분자 모두 용액 상태보다 박막 상태에서 분자 내 전하 전달(intramolecular charge transfer, ICT) 피크에서 흡광도가 넓어지는 것을 관찰할 수 있다.21 특히, 전자 주개인 싸이오펜에 electron-rich group인 methoxy가 치환된 고분자는 그렇지 않은 고분자보다 0-0 peak에서 장파장으로 크게 넓어지는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.22,23 PTDPPOD-Meth는 vibrational peak (0-0)의 구분이 약해지는 반면, PTDPPOD-Th와 PTDPPsi-Meth는 0-1 peak의 구분이 선명해지는 것을 확인하였다. 박막상태에서의 특징 차이를 살펴보면, PTDPPOD-Th와 PTDPPOD-Meth의 vibrational peak의 강도는 서로 상반되는 양상을 띄는 반면, PTDPPsi-Th은 PTDPPsi-Meth와 다르게 vibrational peak가 관찰되지 않고, 흡광도만 넓어지는 것을 관찰할 수 있었다.21,23
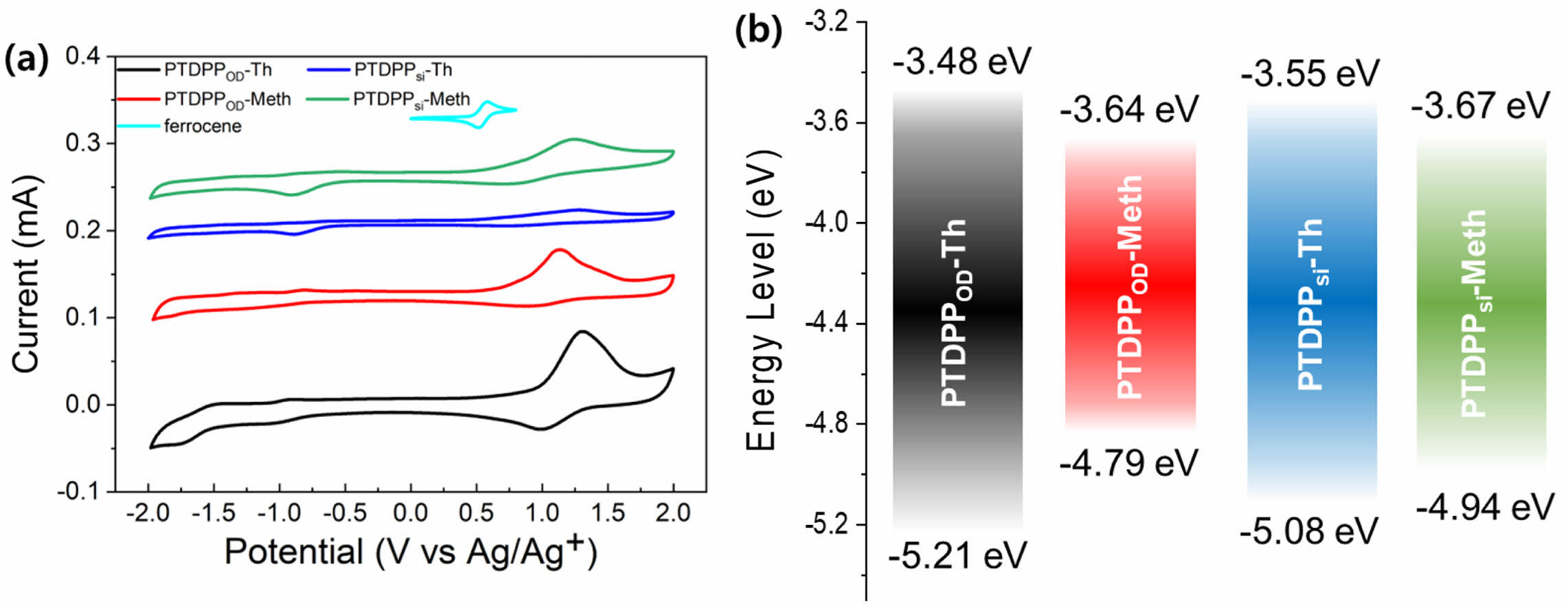
전기화학적 특성. 순환전압전류곡선(cyclic voltammetry curve)을 측정하여 고분자의 전기화학적 특성을 분석하였으며, 자세한 실험과정은 ‘시약, 재료, 기기’ 부분에 나타내었다. 순환전압전류곡선과 에너지 준위를 비교한 그래프는 Figure 4(a)와 (b)에 각각 나타냈으며, 각 고분자의 에너지 준위를 나타낸 결과는 Table 1에 정리하였다. 식 (1), 식 (2)에 대입하여 고분자의 highest occupied molecular orbital(HOMO)와 lowest unoccupied molecular orbital(LUMO) 에너지 준위를 각각 계산하였으며 PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th와 PTDPPsi-Meth의 각각의 HOMO/LUMO 에너지 준위 값은 -5.21/-3.48, -4.79/-3.64, -5.08/-3.55, -4.94/-3.67으로 그리고 전기 화학적 밴드갭은 1.73, 1.15, 1.53 그리고 1.27 eV으로 관찰하였다.23,24
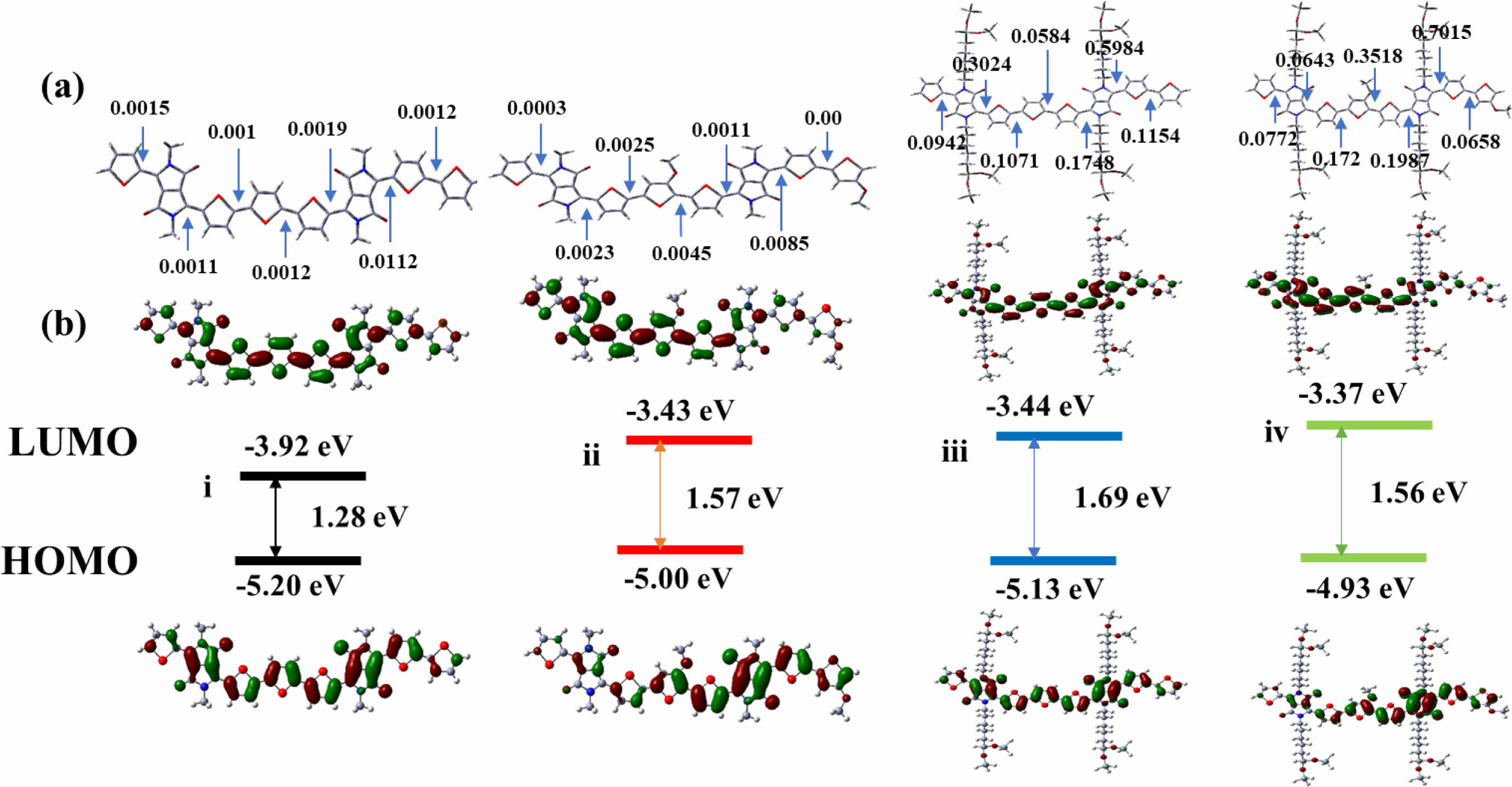
밀도 범함수 이론(Density Functional Theory, DFT). PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th와 PTDPPsi-Meth의 바닥 상태(ground state)와 들뜬 상태(excited state)에서 고분자가 가지는 계산된 최적화된 분자 구조 및 전하 밀도, 에너지 전위 및 광학적 특성을 확인하기 위해 Gaussian 16W 프로그램의 DFT, B3LYP, 6-31G basis set의 설정으로 계산을 진행하였다. 계산 시간 단축을 위해 PTDPPOD-Th와 PTDPPOD-Meth의 선형 곁사슬(octyldodecyl side chain)은 메틸기(methyl group)로 치환해 계산하였고, 전하밀도 입방면체(charge-density isosurfaces), 에너지 준위(energy level), 이면각(dihedral angle)은 Figure 5에 나타내었다. 바닥상태에서의 charge-density isosurfaces는 HOMO energy level에서 LUMO energy level로 갈수록 전자받개 부분에 비편재화되는 것을 확인하였는데, 이것은 methoxy기가 도입된 PTDPPOD-Meth와 PTDPPsi-Meth에서 잘 관찰되었다. 고분자 모두 전자주개와 전자받개와의 intramolecular interaction으로 인한 좋은 평형성(planarity)을 갖는 것을 확인하였다. Self-consistent field density-functional theory(TD-SCF) DFT계산을 통해 UV-Vis 흡수 스펙트럼을 구하였고, PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th와 PTDPPsi-Meth의 최대흡수 파장은 각각 800, 840, 827, 그리고840 nm로 Figure S4에 나타내었다. PTDPPOD-Meth와 PTDPPsi-Meth의 흡광도가 PTDPPOD-Th와 PTDPPsi-Th 보다 넓어지는 것을 확인하였고, 이는 methoxy기의 도입으로 인한 현상이라 예상되었으며 실험으로 측정한 광학적 특성과 일치하는 것을 알 수 있었다.
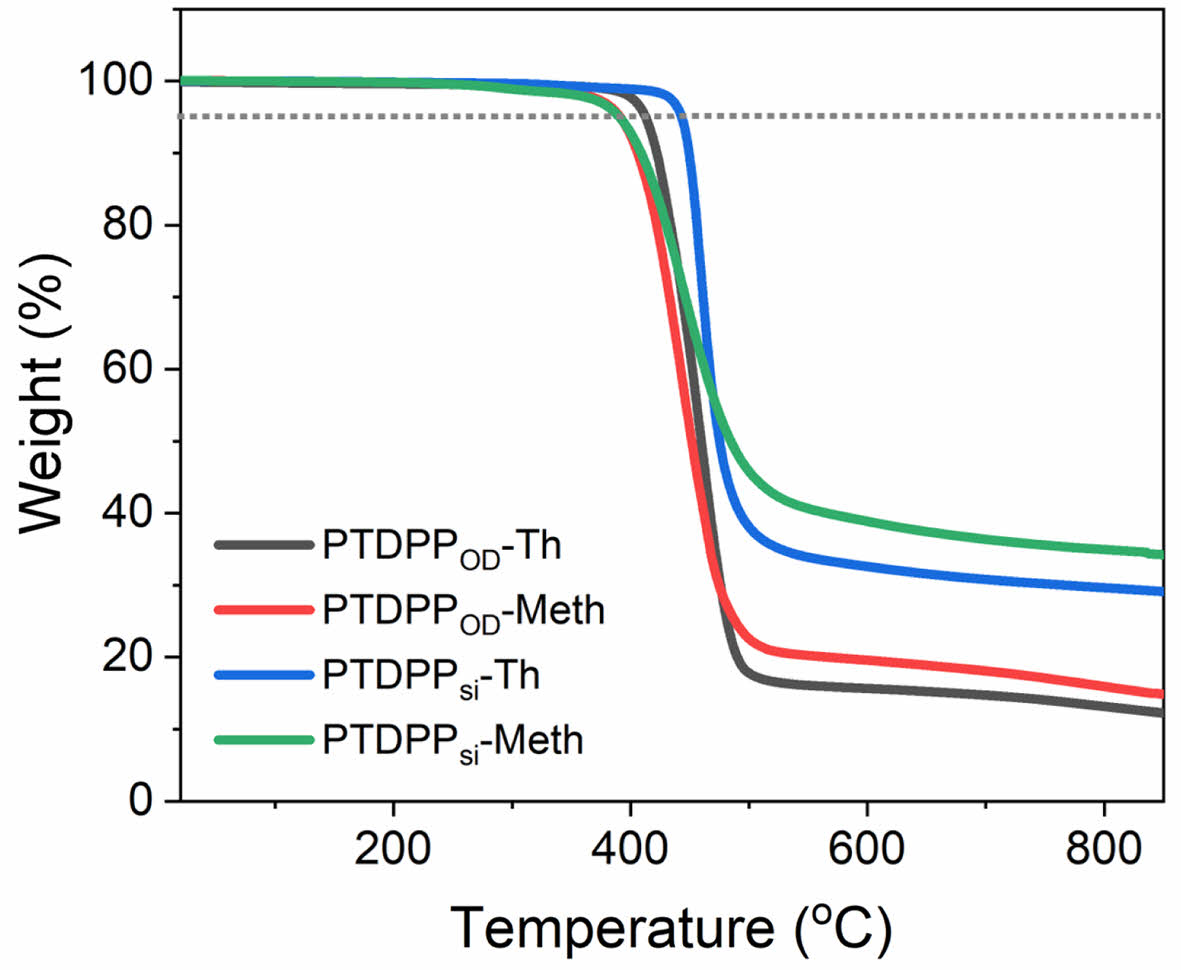
고분자 열적분석. 합성한 고분자의 열적 안정성을 확인하기 위해 열분해온도를 측정하여 확인하였다. TGA를 이용하여 질소 분위기에서 상온(16 ℃)에서부터 900 ℃까지의 온도범위로 10 ℃/min의 속도로 승온하였을 때 온도에 따른 질량 감소율을 측정하고 Figure 6와 Table 1에 나타냈다. 고분자의 열분해 온도(decomposition temperature, Td) 값은 5% 중량 감소율을 보인 지점을 측정하였으며, PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th, PTDPPsi-Meth의 Td 값은 410, 383, 441, 383 ℃으로 확인하였다. 싸이오펜을 단량체로 갖는 고분자 PTDPPOD-Th와 PTDPPsi-Th는 methoxy 싸이오펜을 갖는 고분자 PTDPPOD-Meth보다 더 높은 Td 값을 갖는 것을 확인하였고 이는 열적으로 더 안정하다는 것을 확인하였다.
|
Figure 1 1H NMR spectra for (a) PTDPPOD-Th; (b) PTDPPOD-Meth; (c) PTDPPsi-Th; (d) PTDPPsi-Meth. |
|
Figure 2 Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra for (a) PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth; (b) PTDPPsi-Th and PTDPPsi-Meth |
|
Figure 3 Normalized UV-Vis-NIR absorption spectra of PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th and PTDPPsi-Meth: (a) in dilute chloroform solution; (b) as thin films on a quartz plate. |
|
Figure 4 (a) Cyclic voltammograms; (b) energy diagram of PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th and PTDPPsi-Meth. |
|
Figure 5 (a) Density functional theory (DFT) optimized geometries and charge-density isosurfaces and values of HOMO and LUMO levels of PTDPPOD-Th (ⅰ), PTDPPOD-Meth (ⅱ), PTDPPsi-Th (ⅲ) and PTDPPsi-Meth (ⅳ); (b) Calculated dihedral angles of model dimers. |
|
Figure 6 TGA of PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th and PTDPPsi-Meth under N2 and heating rate of 10 ℃/min. |
|
Table 1 Electrochemical Properties of Polymers |
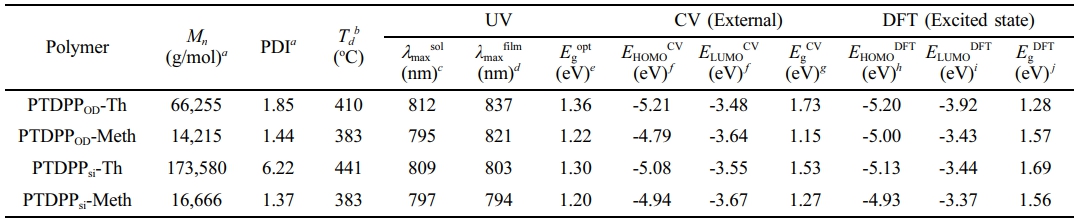
aMn and PDI of polymer were determined by gel permeation chromatography (GPC). b5% weight loss temperature measured by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) under N2. cChloroform solution. dSpin-coated from chloroform solution. eCalculated from the absorption band edge of the polymer film, Egopt =1240/λedgefilm. fcyclic voltammetry determined with (EHOMO=− (Eoxionset− E1/2(Ferrocene) + 4.8 eV) and ELUMO=−(Eredonset − E1/2(Ferrocene) + 4.8 eV). gEgCV=ELUMO−EHOMO; calculated. hHOMO. iLUMO energy levels. jBand gap energy by TD-SCF DFT calculation. |
본 연구진은 DPP 기반한 신규 공액 고분자 4종(PTDPPOD-Th, PTDPPOD-Meth, PTDPPsi-Th와 PTDPPsi-Meth)을 Stille 커플링 중합법으로 성공적으로 합성 정제하였고 실록세인과 methoxy 기에 따른 물리, 화학적 특성을 확인하였다. 실록세인을 갖는 고분자의 경우는 탄화수소를 갖는 고분자에 비하여 넓은 흡수 범위와 높은 열적 안정성을 갖는 것을 확인하였다. 이러한 결과는 다양한 유기 전자 소자에서 고안정성 유기 반도체 재료로 광범위하게 활용할 수 있을 것으로 기대한다.
- 1. Burroughes, J. H.; Bradley, D. D. C.; Brown, A. R.; Marks, R. N.; Mackay, K.; Friend, R. H.; Burns, P. L.; Holmes, A. B. Light-emitting Diodes Based on Conjugated Polymers. Nature 1990, 347, 539-541.
-

- 2. Onimura, K.; Matsushima, M.; Yamabuki, K.; Oishi, T. Synthesis and Properties of N-substituted Maleimides Conjugated with 1,4-phenylene or 2,5-thienylene Polymers. Polym. J. 2010, 42, 290-297.
-

- 3. Jin, R.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, W. Theoretical Studies of Photophysical Properties of D−π−A−π−D-Type Diketopyrrolopyrrole-Based Molecules for Organic Light-Emitting Diodes and Organic Solar Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 667.
-

- 4. Yu, D.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, M.; Fan, Q.; Su, W.; Li, X.; Tan, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhu, W. Synthesis and Photovoltaic Performance of DPP-based Small Molecules with Tunable Energy Levels by Altering the Molecular Terminals. Dyes Pigm. 2016, 125, 151-158.
-

- 5. Lee, K. C.; Kim, S.; Son, J.; Kong, J.; Yang, C. A Brief Review on Self-Assembled Monolayers in Organic Solar Cells: Progress, Challenges, and Future Prospects. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2025, 7, 946-963.
-

- 6. Cheon, H. J.; An, T. K.; Kim, Y.-H. Diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP)-Based Polymers and Their Organic Field-Effect Transistor Applications: A Review. Macromol. Res. 2022, 30, 71-84.
-

- 7. Yan, X.; Xiong, M.; Li, J.-T.; Zhang, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Yao, Z.-F.; Wang, J.-Y.; Gu, X.; Lei, T. Pyrazine-Flanked Diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP): A New Polymer Building Block for High-Performance n-Type Organic Thermoelectrics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 20215-20221.
-

- 8. Gu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, K.; Kurosawa, T.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, H.; Schroeder, B.C.; Yan, H.; Molina-Lopez, F.; Tassone, C.J.; Wang, C.; Mannsfeld, S.C.B.; Yan, H.; Zhao, D.; Toney, M.F.; Bao, Z. Roll-to-Roll Printed Large-Area All-Polymer Solar Cells with 5% Efficiency Based on a Low Crystallinity Conjugated Polymer Blend. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602742.
-

- 9. Nguyen, T.-Q.; Yee, R. Y.; Schwartz, B. J. Solution Processing of Conjugated Polymers: the Effects of Polymer Solubility on the Morphology and Electronic Properties of Semiconducting Polymer Films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2001, 144, 21-30.
-

- 10. Murthy, L. N. S.; Kramer, A.; Zhang, B.; Su, J.-M.; Chen, Y.-S.; Wong, K.-T.; Vandenberghe, W. G.; Hsu, J. W. P. Energy Levels in Dilute-donor Organic Solar Cell Photocurrent Generation: A Thienothiophene Donor Molecule Study. Org. Electron. 2021, 92, 106137.
-

- 11. Chiou, D.-Y.; Su, Y.-C.; Hung, K.-E.; Hsu, J.-Y.; Hsu, T.-G.; Wu, T.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-J. Thiophene–Vinylene–Thiophene-Based Donor–Acceptor Copolymers with Acetylene-Inserted Branched Alkyl Side Chains To Achieve High Field-Effect Mobilities. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 7611-7622.
-

- 12. Xu, C.; Wang, Z.; Dong, W.; He, C.; Shi, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, M.; Jiang, H.; Deng, Y.; Ye, L.; Han, Y.; Geng, Y. Aggregation Behavior and Electrical Performance Control of Isoindigo-Based Conjugated Polymers via Carbosilane Side Chain Engineering. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 10385-10394.
-

- 13. Zhou, N.; Facchetti, A. Naphthalenediimide (NDI) Polymers for All-polymer Photovoltaics. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 377-390.
-

- 14. Bao, W. W.; Li, R.; Dai, Z. C.; Tang, J.; Shi, X.; Geng, J. T.; Deng, Z. F.; Hua, J. Diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP)-Based Materials and Its Applications: A Review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 679.
-

- 15. Nielsen, C. B.; Turbiez, M.; McCulloch, I. Recent Advances in the Development of Semiconducting DPP-Containing Polymers for Transistor Applications. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1859-1880.
-

- 16. Lee, S.; Yoo, H.; Jeong, S.; Kim, D. H.; Kang, S.-H.; Choi, Y.; Yang, C.; Lee, B. H.; Lee, K. C. Pechmann Dye-Containing Diketopyrrolopyrrole-Based Stretchable Polymer Semiconductors. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, 46, 2500018.
-

- 17. Yu, X.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Gao, C.; Xue, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, D. Intrinsically Stretchable Polymer Semiconductors with Good Ductility and High Charge Mobility through Reducing the Central Symmetry of the Conjugated Backbone Units. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209896.
-

- 18. Hooper, R.; Lyons, L. J.; Mapes, M. K.; Schumacher, D.; Moline, D. A.; West, R. Highly Conductive Siloxane Polymers. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 931-936.
-

- 19. Yao, L.; Rahmanudin, A.; Guijarro, N.; Sivula, K. Organic Semiconductor Based Devices for Solar Water Splitting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1802585.
-

- 20. Lee, J.; Han, A.-R.; Yu, H.; Shin, T. J.; Yang, C.; Oh, J. H. Boosting the Ambipolar Performance of Solution-Processable Polymer Semiconductors via Hybrid Side-Chain Engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9540-9547.
-

- 21. Huang, H.; Yang, L.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T. J. Organic and Polymeric Semiconductors Enhanced by Noncovalent Conformational Locks. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10291-10318.
-

- 22. Shi, C.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Pei, Q. Regioregular Copolymers of 3-Alkoxythiophene and Their Photovoltaic Application. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8980-8986.
-

- 23. Imae, I.; Tada, N.; Harima, Y. Synthesis and Properties of Donor-acceptor-type Polymers Comprising Alkoxy-substituted Bithiophene Units. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 2019, 32, 585-592.
-

- 24. Guo, X.; Liao, Q.; Manley, E. F.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, T.; Shin, Y.-E.; Cheng, X.; Liang, Y.; Chen, L. X.; Baeg, K.-J.; Marks, T. J.; Guo, X. Materials Design via Optimized Intramolecular Noncovalent Interactions for High-Performance Organic Semiconductors. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 2449-2460.
-

- Polymer(Korea) 폴리머
- Frequency : Bimonthly(odd)
ISSN 2234-8077(Online)
Abbr. Polym. Korea - 2024 Impact Factor : 0.6
- Indexed in SCIE
 This Article
This Article
-
2025; 49(5): 634-641
Published online Sep 25, 2025
- 10.7317/pk.2025.49.5.634
- Received on Apr 2, 2025
- Revised on May 3, 2025
- Accepted on May 5, 2025
 Services
Services
Shared
 Correspondence to
Correspondence to
- Junghoon Lee* , and Kyu Cheol Lee
-
Department of Applied Chemistry, Dong-Eui University, 176 Eomgwangro, Busan 47184, Korea *Division of Chemical Engineering, Dongseo University, Busan 47011, Korea
- E-mail: junghoonlee@gdsu.dongseo.ac.kr, kclee@deu.ac.kr
- ORCID:
0000-0003-2638-851X, 0009-0004-0429-0452








 Copyright(c) The Polymer Society of Korea. All right reserved.
Copyright(c) The Polymer Society of Korea. All right reserved.